# Common Business Optimization
# List and Long Copy Optimization
Description
Optimization methods for long lists and long copy (e.g., lengthy privacy agreements, user agreements) during display
List
When rendering a list initially, if the content exceeds 10 items, it is recommended to use pagination or trigger new data requests upon reaching the bottom. Avoid rendering a large amount of data initially, as it can cause page rendering lag.
Long Copy
Long copy typically involves displaying a large amount of text on small device screens, such as "User Agreement," "Privacy Agreement," "Minor Protection Agreement," etc.
- It is usually recommended to display the agreement link via a QR code. Scanning the code to view on a mobile device is a common design practice.
- If the product requires full rendering at once, it may cause page rendering lag and affect the initial user experience. Here, chunked rendering of the copy is recommended. Below is a code example:
<!-- Area for rendering the copy, with handleScroll scroll listener bound -->
<template>
<scroll id="scroll" scroll-y="true" class="scroll" onscroll="handleScroll">
<div id="content" class="connent">
<block if="{{currentKey >= 0}}">
<text class="header-1">{{contentArray[0]}}</text>
</block>
<block if="{{currentKey >= 1}}">
<text class="header-1">{{contentArray[1]}}</text>
</block>
<block if="{{currentKey >= 2}}">
<text class="header-1">{{contentArray[2]}}</text>
</block>
</div>
</scroll>
</template>
<!-- Save the copy content as an array and record the sequence number of the currently rendered copy -->
<script>
export default {
data:{
contentArray:[
{
content:'Copy one..........'
},
{
content:'Copy two..........'
},
{
content:'Copy three..........'
}
],
// Current sequence number of the rendered copy
currentKey:0,
// Current total height
currentTHEight:0,
}
// Assign initial value to current total height onReady
onReady(){
this.$element('content').getBoundingClientRect({
success: (data) => {
const { height } = data;
this.currentTHEight = height
}
})
}
// Real-time judgment of scroll height vs. total height; load next copy if near bottom, and reassign total height
handleScroll(e) {
if(currentTHEight - e.scrollY <40){
this.currentKey = currentKey + 1
}
this.$element('content').getBoundingClientRect({
success: (data) => {
const { height } = data;
this.currentTHEight = height
}
})
}
}
</script>
# Swiper Multi-Image Optimization
Description
When using the swiper carousel, if there are many images, avoid rendering multiple images simultaneously. Ensure only images within and around the visible area are rendered.
Suppose an album has 200 images to display, creating 200 sub-components in the swiper is not performance-friendly. Therefore, consider displaying only 3 sub-components in the swiper and dynamically updating the images in the sub-components during swiping to achieve lazy loading in the Swiper. The main process for right-swipe lazy loading is as follows:
Right-Swipe Lazy Loading Process Assume an array of
5imagesdata=[0,1,2,3,4]needs to be displayed in aswiperwith3sub-components.- When the user clicks the first image, the
swiperdata isdata[0], data[1], data[2] - When swiping from the first to the second image, the
swiperarray remainsdata[0], data[1], data[2] - When swiping from the second to the third image, modify the first component's data in the
swiperto the next data of the third imagedata[3], and set theloopproperty of theswiperto true. At this point, theswiperdata isdata[3], data[1], data[2]; - When swiping from
data[3]todata[4], note thatdata[4]is the last data. If the last data is not in the last component of theswiper, reset all data in theswipertodata[len-3], data[len-2], data[len-1]to ensure the last image is in the last component of theswiper, and setlooptofalseto prevent swiping from the last to the first image.
- When the user clicks the first image, the
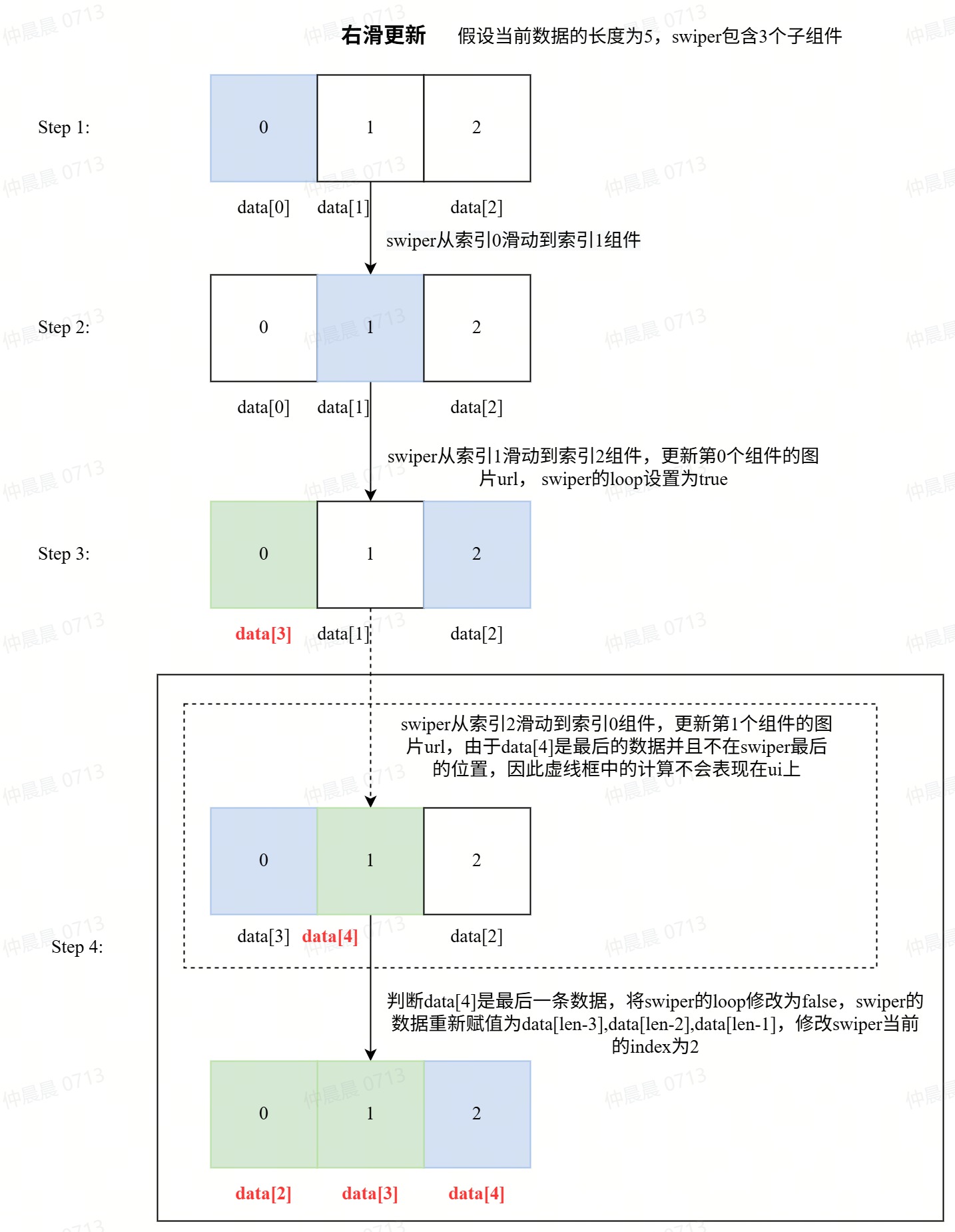
Swiper Lazy Loading Example- Specific Implementation Idea
Monitor the swiper's swiping via the @change event in the code. The logic for judging left and right swipes is as follows:
// Judge right swipe
if (
(!(this.currentIndex === 0 && index === length - 1) && index > this.currentIndex) ||
(index === 0 && this.currentIndex === length - 1)
) {
}else{
}
The logic for right swiping is as follows:
// Update data index
this.dataIndex = this.dataIndex + 1
// Update next right swipe index
const updateIndex = this.dataIndex + 1
if (updateIndex < this.bigThumbnailInfo.length) {
// Update next right swipe to the next image
updateItem = this.bigThumbnailInfo[updateIndex]
// If swiping from the first image
if (this.currentIndex === 0) {
// Before swiping, it's the first image; update the last in swiper after right swipe
this.data[length - 1] = updateItem
resIndex = length - 1
} else {
// console.info("Right swipe: update left")
this.data[this.currentIndex - 1] = updateItem
resIndex = this.currentIndex - 1
}
}
The logic for left swiping is as follows:
// Update data index
this.dataIndex = this.dataIndex - 1
// Update next right swipe index
const updateIndex = this.dataIndex - 1
// Update next left swipe to the previous image
updateItem = this.bigThumbnailInfo[updateIndex]
if (this.currentIndex === length - 1) {
// Before swiping, it's the last image; update the first in swiper after left swipe
this.data[0] = updateItem
resIndex = 0
} else {
this.data[this.currentIndex + 1] = updateItem
resIndex = this.currentIndex + 1
}
Judge if the current image is the last one:
this.data = [
this.bigThumbnailInfo[len - 3],
this.bigThumbnailInfo[len - 2],
this.bigThumbnailInfo[len - 1]
]
indexTemp = 2
this.swiperIndex = this.currentIndex
this.isloop = false
Judge if the upcoming image is the first one:
this.data = [
this.bigThumbnailInfo[0],
this.bigThumbnailInfo[1],
this.bigThumbnailInfo[2]
]
indexTemp = 0
this.swiperIndex = this.currentIndex
this.isloop = false
If it's neither the first nor the last image, set the swiper's loop to true:
this.isloop = true
# Device Frame Rate Optimization Suggestions
- When there are background images or images, minimize the use of
border-radiusand use images with rounded corners instead. - Ensure the image size matches the size of the
divorimagecomponent to avoid scaling. - Reduce modifications to
dynamic styles. - Minimize the
nesting levelof tags. - Reduce reflows and repaints.
# Other Optimization Suggestions
- Add try-catch blocks to catch exceptions.
- For scenarios with slow data requests, consider adding a loading indicator.
